What is the Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol (IBC)?
Mục lục bài viết
The importance of multichain interoperability
The blockchain industry is experiencing a renaissance of development and community engagement. As more projects, use cases, and innovative deployments enter the space, there is a consistent need for the specialized functionality, or certain scalability, that tailor‐made networks can provide.
It’s commonly understood that the value of a system is greater than the sum of its parts. For example, in the case of sovereign nations, each country can feasibly provide for its residents on its own, but may have surpluses of one resource or not enough of another. A global trade network provides more value than the sum of its international parts, with the ability to easily trade surpluses of necessary goods providing more value to citizens than the creation of those goods on their own. Blockchains are no different in this sense, and interoperability between chains with distinct use cases can drive a greater utility than the sum of their parts.
One example of the larger benefit of this shared interoperability is superfluid staking using IBC, a feature that will in the future be enabled on Osmosis. Using Osmosis as the user interface, token holders will be able to deposit any two participating networks’ supported tokens into an Osmosis liquidity pool, and can then stake their liquidity shares to validators on the tokens’ home chains.
In doing so the deposited asset will not only earn its share of fees from the liquidity pool’s swap transactions, but will also earn rewards from helping secure the chain, allowing users to simultaneously provide liquidity to the Osmosis AMM and still participate in the native ecosystems of the tokens they hold by staking. For example, an OSMO<>AKT pool’s LP tokens will be able to secure the network and earn staking rewards on both the Osmosis and Akash networks. This aligns the incentives of both those interested in governance and security of the chain with those that are looking for opportunities to generate high rewards.
This is important in part because a blockchain networks’ security is proportional to the amount of value locked in them. However, because most independent blockchains are not yet fully interoperable, users frequently choose to exchange or swap their tokens, leaving one blockchain ecosystem to explore opportunities in another, or choosing to invest in higher‐yield opportunities instead of participating in securing a network directly via staking. This allows users to not have to choose between earning liquidity rewards and actively participating in the networks whose values and functions they want to help secure.
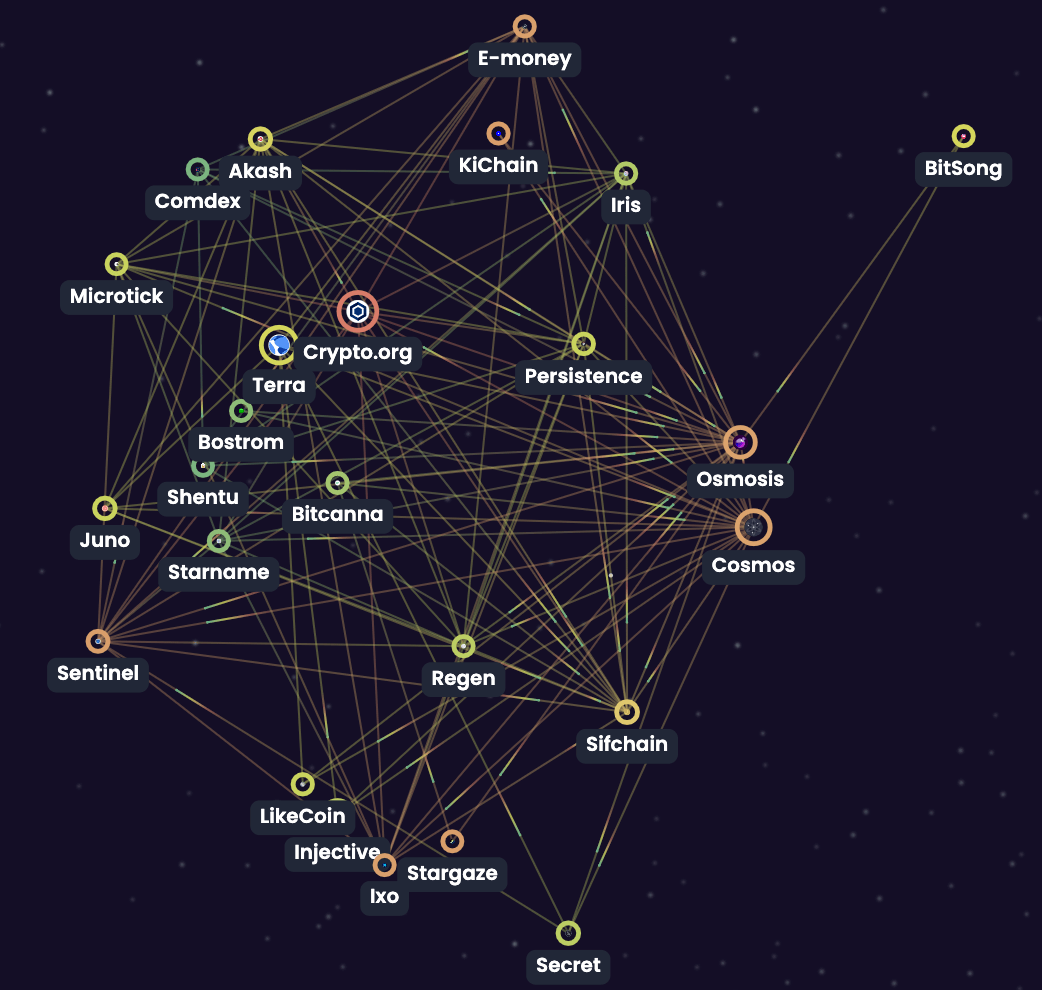
Visual of interchain channels and live IBC transfers from Map of Zones











