2 Main Types of Software with Examples
While working on a computer, we come across various computer software which
helps to ease our tasks and increase the overall efficiency of the work
process. Anything from creating a simple document to surfing the Internet on
a computer system is done using the software.
In this digital or technological era, we are surrounded by different
software, which is even increasing rapidly day by day. No matter what
operating system or platform we use, we are leveraging software and making
our lives easier. Without software, a computer is nothing but a set of
different hardware components.
In this article, we are discussing the different types of software used on
computer systems. However, they are quite similar to each other electronic
devices. Before we discuss the software types, let us understand a quick
introduction to computer software along with its definition:
What is Software?
By definition, “
Software is defined as a collection of data, instructions, programs,
and rules that instruct a computer system or other electronic device to
work efficiently, perform, and carry out specific tasks.
”
In other words, software is a general term that refers to any application,
program, or script running on computer devices to help them perform specific
tasks or process them. It is considered to be the variable part of the
computer system, while the other major part is the hardware which is the
invariable part.
How does Software work?
Computer software is nothing but a separate term for the computer program,
which means some specific set of instructions. Instructions are written in
different languages that can be understood by the computer. Instructions
(commonly called codes) help in giving instructions to the computer to work
and feed data to do the work and satisfy the needs of the users.
The basic logic of all software is to take inputs, process them and provide
output, i.e. Input > Process > Output. For example, consider clicking
the Print button on a computer. The computer takes the document as an input,
then asks users to adjust certain preferences. Thereafter, the given set of
rules is processed and output is provided from the printer as a printed
document on paper.
How many types of Software are there in computers?
There are different types of software based on their classification.
However, if we broadly classify the types of software in a computer, there
are two major types as listed below:
• System Software
• Application Software
Also Read
:
Difference Between System Software and Application Software
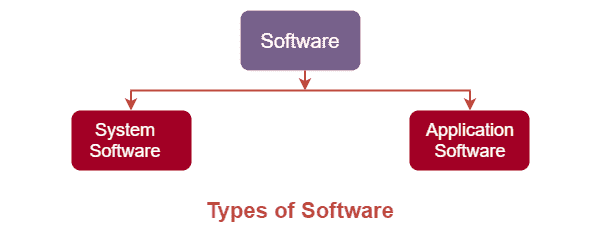
These are the two primary types of software and all other types of software
are served under them. Let us understand both system software and
application software in detail with their types and examples:
Mục lục bài viết
What You Will Learn
System Software
System software is usually defined as a set of various programs or
instructions that help to control or manage the hardware devices connected
to the computer and other important resources of the system. Specifically,
it helps in making the working of the computer efficient, enables faster
performance in a secure manner. In addition, the system software also
establishes a platform to run the application software.
System software allows users a variety of options to interact with basic
settings and to give commands to the computer using a graphical user
interface. Users can only interact with general system settings and
services. In addition, the core services and programs of system software
automatically work in the background to manage system processes and
performance.
Characteristics of System Software
The following are the main characteristics or features of the system
software:
• System software is more closely related to system or hardware
components rather than users.
• System software is much faster in performance or processing.
• System software is usually written or developed in a low-level
language so that it can interact with machines at the maximum possible
speed.
• System software does not interact much with the users as compared
to application software. They usually work in the background.
• It is comparatively difficult to manipulate system software as it
is complex to understand or design.
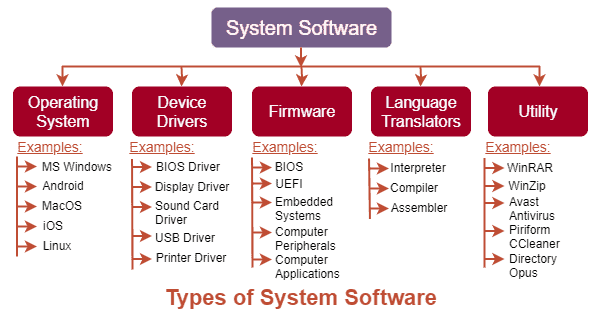
Types of System Software
Now, we already have an idea of what is system software and what are its
features. Let us now understand the different types of system software and
examples, which will help us to understand a little more about system
software:
Operating System:
An operating system, commonly referred to as an OS, is one of the primary types or examples of system software. It consists
of a set of software designed to handle computer resources and services and
provides a platform for running other applications/software.
Although each operating system operates on programming code and
instructions, most operating systems include a GUI (Graphical User
Interface) that helps users to interact with the OS easily without using
coding directly.
Every electronic device, be it a desktop, laptop, or mobile phone, needs to
have an operating system installed on it to function and provide basic
functionality. The operating system is the first program that runs after the
computer system is booted. The operating system takes control of the entire
computer and efficiently manages all services and resources, such as CPU, memory, storage devices (HDD or SSD), printers, etc.
Some of the popular examples of Operating Systems are listed below:
• MS- Windows
• Android
• macOS
• iOS
• Linux
• Ubuntu
• Unix
• CentOS
Device Drivers:
A device driver is specialized computer software primarily designed to
control specific hardware of a computer system. Computers use different
hardware devices, and each device requires a driver to function
properly.
The most common hardware devices that require device drivers are displays,
graphic cards, sound cards, hard disks, printers, mouse, and keyboards. Users may need to manually install device drivers for some hardware
devices, while for others, the operating system automatically installs a
supported driver. There are two different types of device drivers, namely
Kernel Device Drivers
, and
User Device Drivers
.
Some of the popular examples of Device Drivers are listed below:
• BIOS
Driver
• Motherboard Driver
• Display Driver
• Sound Card Driver
• Graphics Card Driver
• Printer Drivers
• VIRTUAL Device Drivers
• ROM Drivers
Firmware:
Firmware is known as permanent software or instructions stored in the
motherboard storage or ROM (read-only memory) of the computer system.
However, it is not actually stored permanently as most current computer
systems allow users to update the firmware using a firmware updater.
Firmware Software, like other software, has a set of instructions. Unlike
other software, the primary function of firmware is to check for errors, and
ensure that all necessary hardware devices are working properly as soon as
the user turns on the computer. If everything is working, the firmware wakes
up the system and transfers control to the operating system.
Some of the popular examples of Firmware are listed below:
• BIOS
• UEFI
• Embedded Systems
• Computer Peripherals
• Computer Applications
Programming Language Translators:
Specifically, system software helps convert high-level language code
(human-readable language code) into simple machine-level code and
vice-versa. This conversion is usually performed using programming language
translators or processors.
Programming language translators help convert computer programs written in
high-level programming languages such as Java, C, C++, Python, etc. (also called source code) into instructions that can
be interpreted by machines as object-level code or machine code.
Despite simplifying the code, programming language translators also help to
perform the following tasks: assigning data storage, obtaining diagnostic
reports, obtaining source code and other details related to the program,
identifying system errors during runtime, or rectify, etc.
Examples of programming language translators are listed below:
• Interpreter
• Compiler
• Assembler
Also Read
:
Difference between Compiler and Interpreter
Utility:
Utility tool or software is primarily developed to analyze, optimize,
configure and maintain a computer system or its resources. This usually
helps to support the computer infrastructure smoothly. Utility software
monitors how the operating system is performing and then gives suggestions
or makes changes automatically to improve the functioning and overall
performance of the computer.
Utility software includes various computer software categories, such as
antivirus, disk clean-up, and management tools, performance optimizers,
defragmenters, compression tools, etc.
Some of the popular examples of utility tools/software are listed below:
• Windows File Explorer
• WinRAR
• WinZip
• Avast Antivirus
• McAfee Antivirus
• Norton Antivirus
• Directory Opus
• Piriform Defraggler
• Piriform CCleaner
• Razer Cortex
Application Software
Application software refers to a set of programs and instructions that help
perform specific tasks, on a computer system. It is mainly designed to meet
certain requirements of a particular environment. Application software can
be downloaded and installed manually on the computer system and these
software have nothing to do with the system core functions.
Application software typically runs in the front-end, making it more accessible
and intractable to users. It is important to note that application software
cannot run on its own; they require the platform established by the system
software. For example, any web browser software like Google Chrome requires
an operating system to run. Unlike system software, application software is
not mandatory for the system. However, they can help perform various tasks
on the computer.
Characteristics of Application Software
The following are the main characteristics or features of the application
software:
• Application software is mainly developed or programmed to complete
specific tasks on computers, such as image editing, word processing, gaming,
etc.
• Application software is mostly bigger in size and hence takes up
more storage or space on the machines/systems.
• Application software is typically written or developed in
high-level languages.
• Application software generally interacts more with users, helping
them to use the software easily.
• Application software is somewhat easier to design and develop than
system software.
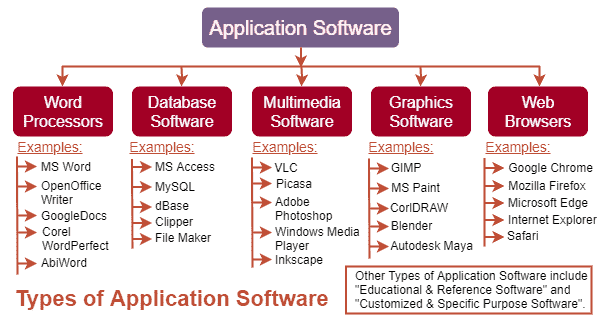
Types of Application Software
Now, we already have an idea of what is application software and what are
its features. Let us now understand the different types of application
software and examples, which will help us to understand a little more about
application software:
Word Processors:
Word processors or word processing software are primarily designed to create
documentation on computers or other electronic devices. Additionally, word
processor software also helps in managing, formatting, and printing
documents.
Some of the popular examples of Word Processors are listed below:
• MS Word
• Google Docs
• OpenOffice Writer
• Corel WordPerfect
• AbiWord
• Apple iWork- Pages
Database Software:
Database software is useful computer software that mainly helps in creating
and managing databases. It is also called DBMS (Database Management
Software). Database software plays an important role when organizing data on
a computer or server.
Some of the popular examples of Database software are listed below:
• MS Access
• MySQL
• dBase
• Clipper
• FileMaker
• FoxPro
Multimedia Software:
As the name suggests, multimedia software is mainly used to perform tasks
related to media files, such as audio or video files. It helps to play,
create or modify media files. Multimedia software plays an important role in
image editing, video editing, animation, and graphics-related tasks.
Some of the popular examples of Multimedia software are listed below:
• Windows Media Player
• Windows Movie Maker
• VLC Media Player
• Picasa
• Adobe Photoshop
• Media Monkey
• Inkscape
Graphics Software:
Graphics software is strictly designed keeping in mind the graphics-related
tasks. It primarily helps users to design logos, edit images, and make other
changes to visual data. Graphics software includes many built-in tools and
features to make editing and illustration easier.
Some of the popular examples of Graphics software are listed below:
• Adobe Photoshop
• Adobe Illustrator
• Adobe Indesign
• CorelDRAW
• GIMP
• MS Paint
• Blender
• Autodesk Maya
Web Browsers:
Web browsers are mainly used for searching the internet or browsing the
internet. It is specialized computer software and helps users to find
specific web addresses to retrieve data across the web.
Most computers and electronic devices come preinstalled with a native web
browser provided by the manufacturer. However, users can always install
desired third-party web-browsers from the App Store using the Internet on
their devices.
Some of the popular examples of Web Browsers are listed below:
• Google Chrome
• Mozilla Firefox
• Microsoft Edge
• Internet Explorer
• Opera
• Safari
Education and Reference Software:
These are computer software primarily designed to help users learn specific
topics on specific subjects. A wide range of educational software is
available on the internet and users can facilitate learning through them.
This type of software is also known as
Academic Software
.
Educational software can be free-to-use or paid. Some of the popular
examples of Educational or Reference software are listed below:
• Delta Drawing
• Polarr
• GeoGebra
• FluidMath
• GCompris
• Tux Paint
• OneNote
• Microsoft To-Do
Customized or Specific Purpose Software:
Customized or specific purpose software is specialized computer software
developed or programmed primarily to perform specific tasks/ functions or
designed for specific organizations. All such software that fulfills
specific purposes comes under application software.
Some of the popular specific purpose software are Railway Reservation
System, Invoice Management System, Airline Reservation System, etc.
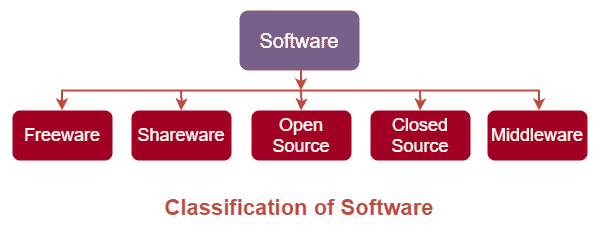
Classification of Computer Software
Apart from the classification mentioned above, there exists another popular
classification of computer software. This classification is generally based
on the availability and shareability of the software, which includes the
following:
• Freeware
• Shareware
• Open Source
• Closed Source
• Middleware
Let us understand each in detail:
Freeware
Freeware is a type of computer software that is freely available on the
Internet. Users do not need to pay anything to use the freeware. They can
easily download the freeware from the official sites of their respective
developer, and install it on the computer like any other normal software.
Apart from this, the freeware does not allow others to edit or modify the
original software without the consent of their owner. Furthermore, no other
person or website may charge for the distribution of the freeware. Some
popular freeware examples are listed below:
• Adobe Reader
• Audacity
• Team Viewer
• Recuva
• CCleaner
• Skype
• Yahoo Messenger
• ImgBurn
Shareware
Shareware is a type of computer software that is freely available to be used
and shared on a trial basis. This means shareware is provided to the users
with a fixed time limit. Once the limit is reached, users will have to
purchase the software or pay monthly to continue using the services.
Shareware may offer all or a limited number of services before the time
limit is reached. Similarly, some services or all services may be restricted
once the limit is reached. Shareware usually allows users to test the
software before purchasing it so that users can check whether the software
is right for them or their business needs.
WinRAR
is one of the most
popular shareware software used on computer systems. Some other popular
shareware examples are listed below:
• Adobe Acrobat
• Winzip
• Getright
• PHP Debugger
Open-Source
As the name suggests, open-source software is provided to the users with the
source code in which the software is written. The source code is shared so
that others can modify the code and add additional features in the software
according to their needs.
The main purpose of open-source software is to encourage developers to show
their potential and creativity. Specifically, open-source means developing
or modifying the code to make it even better for others. Open-source
software can be distributed as free or chargeable by its owner.
Linux OS
is one of the most
popular free-to-use open-source software. Some other essential open-source
software examples are listed below:
• Apache Web Server
• Mozilla Firefox
• Thunderbird
• Moodle
• GNU Compiler Collection
Closed-Source
Closed-source software (also called
proprietary software
) is a type of computer software that does not distribute source code or
native code. No unauthorized moderation is allowed in closed source
software. The source of closed-source software is kept completely private
and encrypted.
Most of the software used on computers is closed-source and asks users to
pay or purchase them. The developer/owner has all rights or registered
patents on the source code of the closed source software. Generally,
closed-source software are developed for commercial use; however, they can
be both commercial and private.
Skype
is one of the most popular
closed-source software and typically charges high-volume users money. Some
other essential closed-source software examples are listed below:
• Google Earth
• WinRAR
• Adobe Flash
• Microsoft Office
• Microsoft Windows
Middleware
As the name suggests, middleware is a type of computer software that usually
mediates between application and system software, or between two different
application software. For instance, middleware helps Microsoft Windows
interact with MS Word or MS Excel.
Middleware can also help send remote work requests between two different
computers, from an application with one specific OS to an application with a
different OS. Also, middleware plays an important role in making new
computer applications/programs work in old or legacy ones.
Some essential middleware software examples are listed below:
• Integration
• Transactions
• Data Access
• Application Framework
• Device Middleware
• Game Engines
• Robot Middleware
Summary
As discussed above, the software is a set of programs used on computer
devices that help the users to give commands to the computer as well as
instruct the computer what to do. The two major types of software include
system software and application software. System software is designed to
manage system resources or operations, whereas application software helps to
meet certain needs of users to perform specific tasks on a computer.











