Arduino – Serial Plotter | Arduino Tutorial
Mục lục bài viết
Arduino – Serial Plotter
About Serial Plotter
Serial Plotter is one of the tools in Arduino IDE. Arduino can read the temperature, humidity or any kind of sensor data, and send it to Serial Plotter. Serial Plotter receives data from Arduino and visualizes data as waveforms. Serial Plotter can visualize not only single but also multiple sensor data in the same graph.
Data is exchanged between Serial Plotter and Arduino via USB cable, which is also used to upload the code to Arduino. Therefore, To use Serial Plotter, we MUST connect Arduino and PC via this cable.
Serial Plotter includes a selection box to select the serial baud rate and a graph:
-
X-axis: represent the time. It has 500 points. The time between each point is the time between two consecutive Serial.println() function calls. This time is usually equal to the time of loop() function.
-
Y-axis: represents the values received from Arduino. The Y-axis automatically adjusts itself as the value increases or decreases.
How To Open Serial Plotter
On Arduino IDE, Go to Tools Serial Plotter
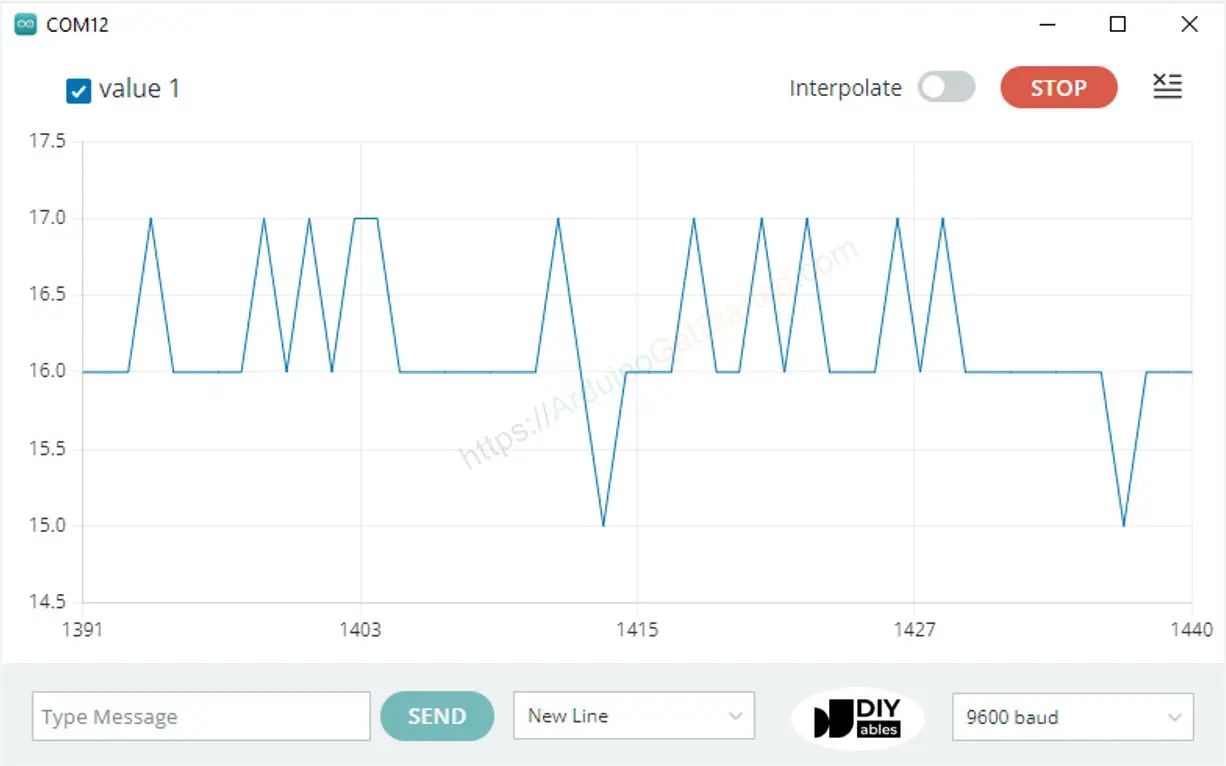
Plotting of Single Line in Graph
To print a single graph, we just need to send the data and terminate it by “\r\n” character.
In detail, we just need to use Serial.println() function
Serial
.
println
(variable);
※ NOTE THAT:
Serial.println() automatically appends “\r\n” characters after data.
Example Code
This example reads the value from an analog input pin and plots them on Serial Plotter
void
setup
() {
Serial
.
begin
(9600);
}
void
loop
() {
int
y1 =
analogRead
(A0);
Serial
.
println
(y1);
delay
(100);
}
Quick Steps
-
Copy the above code and open with Arduino IDE
-
Click
Upload
button on Arduino IDE to upload code to Arduino
-
Open Serial Plotter
-
Select baurate 9600
-
See graph on Serial Plotter
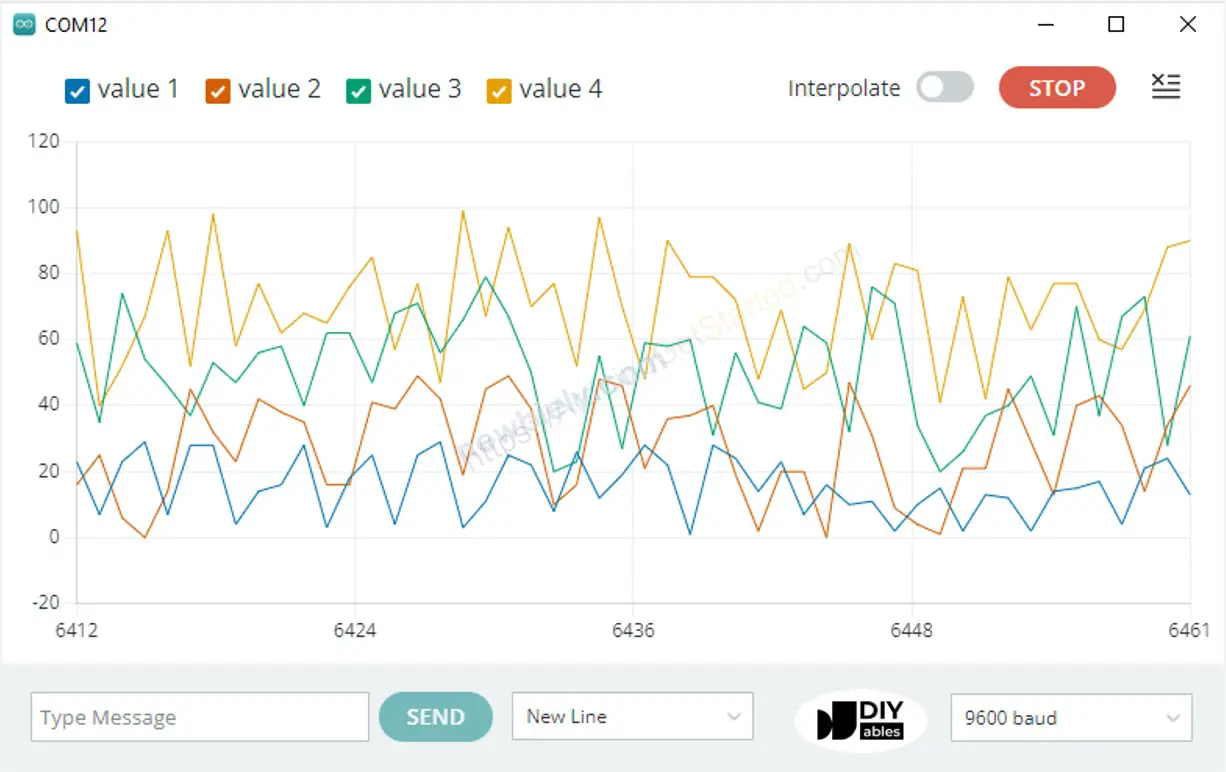
Plotting of Multiple Lines in Graph
When we want to plot multiple variables, we need to separate variables from each other by “\t” or ” ” character. The last value MUST be terminated by “\r\n” characters.
In detail:
-
The first variable
Serial
.
(variable_first);
-
The middle variables
Serial
.
(
“\t”
);
Serial
.
(variable_nth);
-
The last variable
Serial
.
(
“\t”
);
Serial
.
println
(variable_last);
Example Code
This example reads the value from 4 analog input pins and plots them on Serial Plotter
void
setup
() {
Serial
.
begin
(9600);
}
void
loop
() {
int
y1 =
analogRead
(A0);
int
y2 =
analogRead
(A1);
int
y3 =
analogRead
(A2);
int
y4 =
analogRead
(A3);
Serial
.
(y1);
Serial
.
(
” “
);
Serial
.
(y2);
Serial
.
(
” “
);
Serial
.
(y3);
Serial
.
(
” “
);
Serial
.
println
(y4);
delay
(100);
}
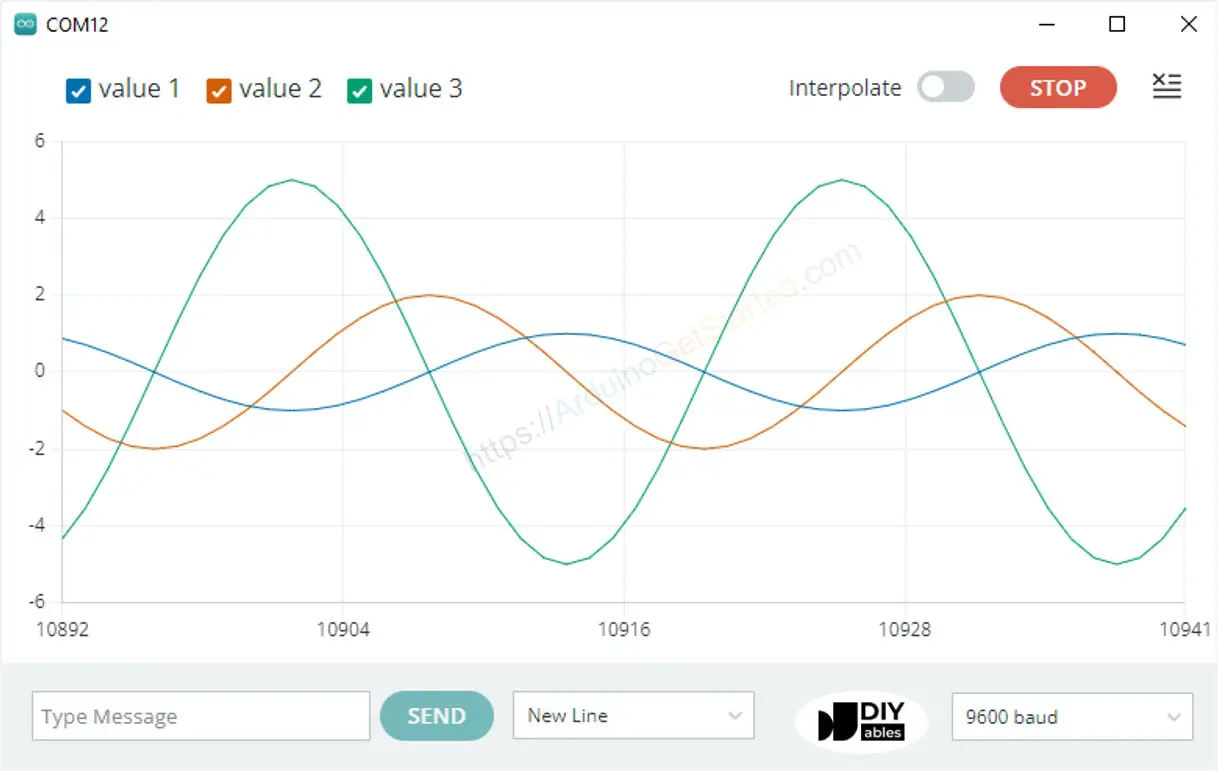
Multiple Graph:
Example of 3 Sine Waveforms
void
setup
() {
Serial
.
begin
(9600);
}
void
loop
() {
for
(
int
i = 0; i < 360; i += 5) {
float
y1 = 1 *
sin
(i * M_PI / 180);
float
y2 = 2 *
sin
((i + 90)* M_PI / 180);
float
y3 = 5 *
sin
((i + 180)* M_PI / 180);
Serial
.
(y1);
Serial
.
(
“\t”
);
Serial
.
(y2);
Serial
.
(
“\t”
);
Serial
.
println
(y3);
delay
(100);
}
}
Multiple Sine Waveform Graph:
Video Tutorial
We are considering to make the video tutorials. If you think the video tutorials are essential, please subscribe to our YouTube channel to give us motivation for making the videos.
Additional Knowledge
-
It’s possible to view the serial plotter on the smartphone or tablet. To do so, you need to use PHPoC WiFi shield
The Best Arduino Starter Kit
-
See the best Arduino kit for beginner
※ OUR MESSAGES
-
We are AVAILABLE for HIRE. See how to hire us to build your project
-
If this tutorial is useful for you, please give us motivation to make more tutorials
-
You can share the link of this tutorial anywhere. Howerver, please do not copy the content to share on other websites. We took a lot of time and effort to create the content of this tutorial, please respect our work!
Follow Us











