Difference between Top-down and Bottom-up Approach (with Comparison Chart) – Tech Differences
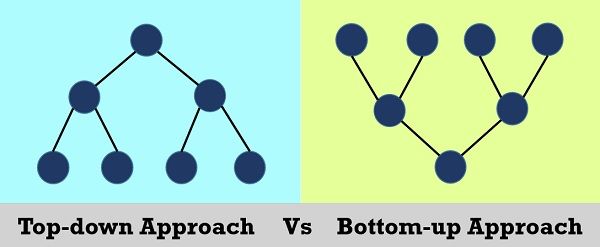 The algorithms are designed using two approaches that are the top-down and bottom-up approach. In the top-down approach, the complex module is divided into submodules. On the other hand, bottom-up approach begins with elementary modules and then combine them further. The prior purpose of an algorithm is to operate the data comprised in the data structure. In other words, an algorithm is used to perform the operations on the data inside the data structures.
The algorithms are designed using two approaches that are the top-down and bottom-up approach. In the top-down approach, the complex module is divided into submodules. On the other hand, bottom-up approach begins with elementary modules and then combine them further. The prior purpose of an algorithm is to operate the data comprised in the data structure. In other words, an algorithm is used to perform the operations on the data inside the data structures.
A complicated algorithm is split into small parts called modules, and the process of splitting is known as modularization. Modularization significantly reduces the complications of designing an algorithm and make its process more easier to design and implement. Modular programming is the technique of designing and writing a program in the form of the functions where each function is distinct from each other and works independently. The content in the functions are cohesive in manner, and there exists a low coupling between the modules.
Mục lục bài viết
Content: Top-down Approach Vs Bottom-up Approach
Comparison Chart
Basis for comparisonTop-down ApproachBottom-up Approach
BasicBreaks the massive problem into smaller subproblems.Solves the fundamental low-level problem and integrates them into a larger one.
ProcessSubmodules are solitarily analysed.Examine what data is to be encapsulated, and implies the concept of information hiding.
CommunicationNot required in the top-down approach.Needs a specific amount of communication.
RedundancyContain redundant information.Redundancy can be eliminated.
Programming languagesStructure/procedural oriented programming languages (i.e. C) follows the top-down approach.Object-oriented programming languages (like C++, Java, etc.) follows the bottom-up approach.
Mainly used inModule documentation, test case creation, code implementation and debugging.Testing
Definition of Top-down Approach
The top-down approach basically divides a complex problem or algorithm into multiple smaller parts (modules). These modules are further decomposed until the resulting module is the fundamental program essentially be understood and can not be further decomposed. After achieving a certain level of modularity, the decomposition of modules is ceased. The top-down approach is the stepwise process of breaking of the large program module into simpler and smaller modules to organise and code program in an efficient way. The flow of control in this approach is always in the downward direction. The top-down approach is implemented in the “C” programming language by using functions.
Thus, the top-down method begins with abstract design and then sequentially this design is refined to create more concrete levels until there is no requirement of additional refinement.
Definition of Bottom-up Approach
The bottom-up approach works in just opposite manner to the top-down approach. Initially, it includes the designing of the most fundamental parts which are then combined to make the higher level module. This integration of submodules and modules into the higher level module is repeatedly performed until the required complete algorithm is obtained.
Bottom-up approach functions with layers of abstraction. The primary application of the bottom-up approach is testing as each fundamental module is first tested before merging it to the bigger one. The testing is accomplished using the certain low-level functions.
Key Differences Between Top-down and Bottom-up Approach
- Top-down approach decomposes the large task into smaller subtasks whereas bottom-up approach first chooses to solve the different fundamental parts of the task directly then combine those parts into a whole program.
- Each submodule is separately processed in a top-down approach. As against, bottom-up approach implements the concept of the information hiding by examining the data to be encapsulated.
- The different modules in top-down approach don’t require much communication. On the contrary, the bottom-up approach needs interaction between the separate fundamental modules to combine them later.
- Top-down approach can produce redundancy while bottom-up approach does not include redundant information.
- The procedural programming languages such as Fortran, COBOL and C follows a top-down approach. In contrast, object-oriented programming languages like C++, Java, C#, Perl, Python abides the bottom-up approach.
- Bottom-up approach is priorly used in testing. Conversely, the top-down approach is utilized in module documentation, test case creation, debugging, etcetera.
Conclusion
The top-down approach and bottom-up approach are the algorithm design methods where top-down is a conventional approach which decomposes the system from high-level specification to low-level specification. On the other hand, the bottom-up approach is more efficient and works in an inverse manner where the primitive components are designed at first then proceeded to the higher level.
The top-down approach emphasizes on the isolation of the submodules (signifies the low coupling between the modules) while ignores the identification of communication and reusability concept. While in the bottom-up approach, information hiding and reusability are the prominent factors.











