How to Install Kali Linux on VirtualBox: An Expert Guide
Kali Linux is a Debian-based Linux distribution developed for penetration testing, and is especially useful for security specialists and enthusiasts. Kali Linux, formerly known as BackTrack Linux, includes a lot of tools and applications for network audits. Kali can be run as a Live DVD, and can be installed on a computer as a host operating system (OS) as any other Linux. However, it is not recommended that you use Kali as a general purpose desktop operating system. At the same time, when using Kali Live DVD, settings are not saved after a system reboot. In this situation, virtual machines can be of great help. Today’s blog post explores how to install Kali Linux on VirtualBox as a virtual machine (VM).
The advantages of installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox are:
- By running multiple operating systems simultaneously (a host OS and a guest OS or multiple guests), you don’t need to reboot a computer as when using dual boot.
- A VM running Kali Linux is isolated from your host OS – running Kali on a VM in an isolated environment is secure.
- You can take a snapshot and roll back to the previous VM state if something goes wrong. The risk of harm to Kali Linux on a VM is minimal as a result.
- You can copy a configured VM on which Kali Linux is installed to other computers.
- You can attach physical USB devices, such as external network adapters directly to a VM due to the VirtualBox USB pass-through feature.
Make sure that VirtualBox is installed on your host operating system before continuing, using the latest VirtualBox version if possible. Please install VirtualBox Extension Pack on your host machine to use some advanced features such as USB pass-through. In the today’s blog post, you will learn how to install Kali Linux on VirtualBox on Windows 10. If you wish to know how to install Kali Linux on VirtualBox on Mac, don’t worry – the installation principle is the same, due to the universality and multiplatform nature of VirtualBox. The installation algorithm is similar as that for installing Ubuntu on VirtualBox.
Mục lục bài viết
Downloading the Installation Image of Kali Linux
First, go to the official web site and download the ISO image of Kali Linux. There are multiple 32-bit and 64-bit images that have different graphical user interfaces (Gnome, KDE, XFCE, LXDE etc.). Let’s download Kali Linux 64-bit v.2019.2 – this distribution has Gnome as a graphical user interface (GUI). You can download images via HTTP and Torrent protocols. Save the ISO file to a custom folder, for example, C:\VirtualBox\kali-linux-2019.2-amd64.iso. You can also verify the SHA256 check sum to make sure that your image is consistent after finishing downloading.

Creating a New VM
Once you have downloaded the installation image, you can create a new VM. Open VirtualBox and create a new VM (Machine > New or Ctrl+N) on which Kali Linux will be installed.

Set the following VM parameters:
Name: Kali_x64
Machine Folder: C:\Virtual\VirtualBox (This path is used only for demo purpose. Try not to use a system partition to store VMs).
Type: Linux
Version: Debian (64-bit)
Memory size: 4096 MB. The VM memory size must be large enough to run a guest OS, though you should leave enough unallocated memory to run your host OS. In the current example, a host machine with 16 GB of RAM is used, which provides enough memory left for a host OS.
Hard disk: Create a virtual hard disk now.
Hit Create to continue and configure a new virtual hard disk.

Set the virtual disk file location, for example C:\Virtual\VirtualBox\Kali_x6Kali_x64.vdi
It is recommended that you store virtual disk files in the VM folder (such folder is selected by default).
Set the virtual disk file size. It should be at least 20 GB.
Hard disk file type: VDI. A native VirtualBox format is selected.
Storage on physical disk: Dynamically allocated (the analog of thin provisioning in VMware).
Click Create to finish creating a new VM.

After creating a new VM, some additional settings must be configured. Select your recently created virtual machine and open the VM settings.

Display options
Go to Display > Screen and set Video Memory to 128 MB. It will prevent installer hanging.
Next, tick the checkbox Enable 3D acceleration (optional). It will be useful for applications that need 3D acceleration.

Network options
Next, go to the network settings and select the networking mode of the virtual network adapter of the VM. Let’s select the Bridged mode to use the VM network adapter much as you would for a physical network adapter of the host machine. In this case, the VM network adapter is connected to the same physical network as the host machine. You can set additional options such as network adapter name, type, MAC address etc.

Boot options
You have to insert your virtual ISO DVD image to a virtual DVD drive of the VM and then boot a virtual machine from that ISO disk. In the VM settings, go to Storage, select an IDE controller of your virtual optical drive (it is empty by default). Click the empty status, then click the disc icon near IDE Secondary Master and in the opened menu, select Choose Virtual Optical Disk File. Browse the Kali Linux installation ISO image that you have downloaded from the official site before (kali-linux-2019.2-amd64.iso). Hit OK to save settings.

The Step-By-Step Process of Installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox
Now you can start your new VM (Kali_x64 in this case) and begin the Kali installation.

After booting from a virtual DVD, you will see a boot menu where you can select boot options for Kali Linux such as Boot from Live DVD, Install, Graphical Install etc. Let’s select Graphical Install. Press Enter to continue.

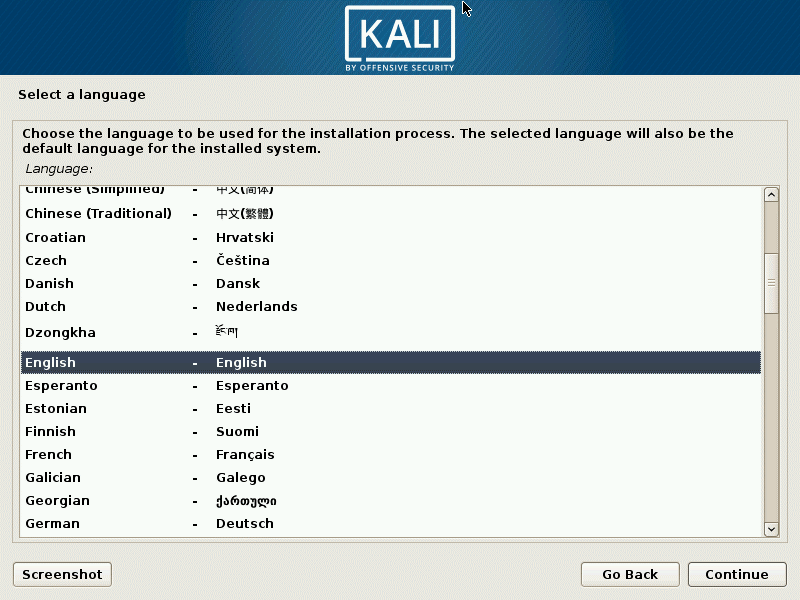
Select a language. Choose the language you wish to use for the installation process and the installed system. English is selected for the current installation. Click the Continue button on each screen to move forward.
Select your location. This option is used to set your time zone, time format, etc. United States has been selected in the current example.

Configure the keyboard. Select your keyboard layout. American English is used for the current installation.

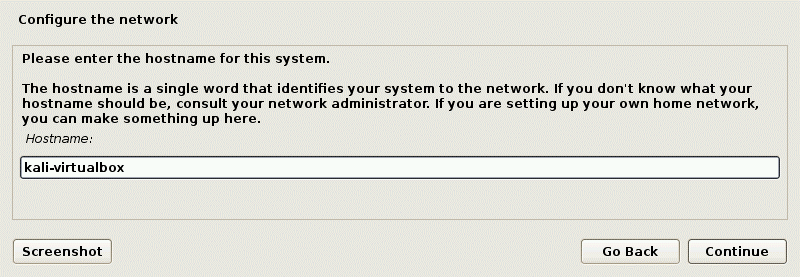
Configure the network. Enter the hostname for your Linux system, for example, kali-virtualbox.
Configure the domain name. If you don’t use a domain in your network, you may leave this field empty.

Set up users and passwords. Read the useful tips on this screen and enter the password for root.

Configure the clock. Now you can select a precise time zone for your country.

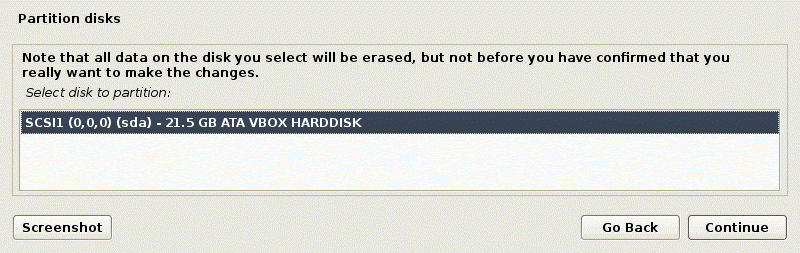
Partition disks. You can use manual and guided partitioning of disks. For the first time, you can select Guided – use entire disk. The entire disk will be used for creating one big partition.

Confirm that you want to erase the disk. There is no reason to worry, as in this case, the empty 20-GB virtual disk is used for partitioning.
Select a preferred partitioning scheme for your virtual disk. Let’s select All files in one partition.

Check the overview and select Finish partitioning and write changes to disk.

Select Yes and confirm that you would like to write changes to the disk.

Wait for the system to be installed. As Kali Linux is being installed, the files are being copied to the virtual disk of the VM.

Configure the package manager. Click Yes if you would like to use a network mirror. Selecting this option will allow you to install or update application packages from online software repositories.

Enter the information about your proxy server if you use a proxy server for internet access from your network. There is no proxy server in this example; so this field is left empty.

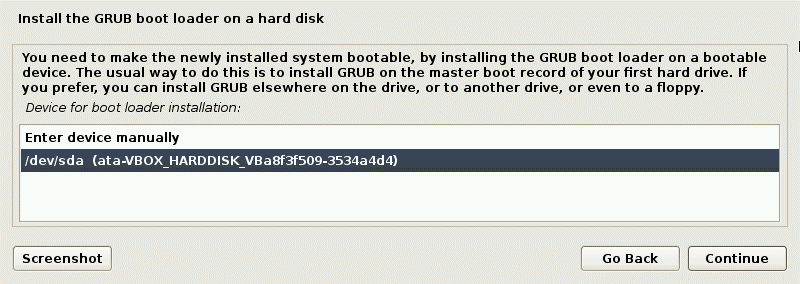
Install the GRUB boot loader on a hard disk. Since there is no other operating systems and boot loaders on a virtual disk, it is necessary to install GRUB in this case. Select Yes to install GRUB.

Select a disk to which GRUB must be installed. In this case, /dev/sda is the necessary disk and is the only disk connected to a VM.
Finish the installation. When the installation of Kali Linux on VirtualBox is complete, you will see a notification message. Now you can reboot the virtual machine to boot the Kali Linux installed on the VirtualBox VM.

After the reboot, you will see a login screen of Kali Linux. Enter root as a user name, then enter the password set during installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox to sign in.

Now you should see the Gnome desktop of Kali Linux installed on your VirtualBox virtual machine.

Installing VirtualBox Guest Additions on Kali Linux
You can install VirtualBox guest additions by inserting the ISO image located in the VirtualBox installation folder by default, or you can install Guest Additions from online Linux repositories by using your Linux package manager.
Update the package repositories tree.
apt-get update
Install VirtualBox Guest Additions with the command:
apt-get install -y virtualbox-guest-x11
![]()
After that, you should reboot the machine.
init 6
Verify that VirtualBox Guest Additions have been installed successfully. Check the VirtualBox Guest Additions version by getting information about the appropriate Linux kernel module. In order to see general information about the vboxguest module, use the command:
modinfo vboxguest
If you want to see the version of VirtualBox Guest Additions only, use:
lsmod | grep -io vboxguest | xargs modinfo | grep -iw version

After installing VirtualBox Guest Additions on a VM, go to VM settings > General > Advanced and enable shared clipboard and Drag n Drop in the bidirectional mode.

Connecting the USB Wi-Fi Adapter to the Kali Linux VM in VirtualBox
After making the general VM configuration, let’s connect an external USB Wi-Fi network adapter to the VirtualBox VM running Kali Linux. You will be able to use all the advantages of the physical USB Wi-Fi adapter in the VM running Kali to make the audit of wireless networks. VirtualBox Extension Pack must be installed to continue configuring the VM.
Insert your USB Wi-Fi adapter to the USB port of your physical computer. Open VM settings and go to the USB section. Tick the checkbox Enable USB Controller, Select USB 2.0 (EHCI) Controller (the Wi-Fi adapter used in the current example has USB 2.0 interface). Then, add the plus icon and select the necessary USB device from the list of USB devices connected to your host machine. Later, you can untick the checkbox near the added USB device if that device does not need to be attached to the VM.

Start your Kali_x64 VM and login to Kali Linux. Open console (Terminal) and run the command to check your network interfaces and their configuration.
ifconfig

The USB Wi-Fi adapter is connected and the name of its interface is wlan0. Let’s change the MAC address to go unnoticed.
Shutdown the Wi-Fi network interface.
ifconfig wlan0 down
Change the MAC address of the wireless network adapter – set the random MAC address with macchanger.
macchanger -r wlan0
Enable the wlan0 network interface.
ifconfig wlan0 up
Check whether the MAC address of your Wi-Fi network interface has been changed.
macchanger -s wlan0
ifconfig wlan0

The MAC address has been changed successfully.
Enable the monitor mode for your wireless network interface with airmon-ng (by default a Wi-Fi adapter works in the managed mode). The monitor mode is required for security testing of Wi-Fi networks.
airmon-ng start wlan0
If there are any processes that could cause trouble, kill them with the command:
airmon-ng check kill
After that run the airmon-ng start wlan0 command once again.

After starting the monitoring mode, a virtual wlan0mon network interface is created. You can also change the MAC address of the wlan0mon network interface to a random MAC address.
ifconfig wlan0mon down
macchanger -r wlan0mon
ifconfig wlan0mon up
Now run the airodump-ng utility to view the networks which signal level allow to test them.
airodump-ng wlan0mon
As you can see on the screenshot below, a physical USB Wi-Fi adapter connected to the virtual machine running Kali Linux works fine. Wi-Fi access points and associated clients are displayed in the console.

Now that you know how to Install Kali Linux on VirtualBox manually and how to configure a wireless network adapter for using it in Kali Linux, you can continue testing Wi-Fi networks but further configuration of Kali Linux for testing wireless networks is out of scope for today’s blog post.
How to Install Kali Linux on VirtualBox with an OVA Template
In the sections above, manual installation of Kali Linux on VirtualBox VMs was explained. There is one more method you can use to install Kali Linux on VirtualBox VMs – deploying an OVA template. Deploying VMs from VM templates has a list of advantages – you can deploy multiple similar pre-configured VMs from the template and save the time otherwise needed to install an operating system and applications. There are official pre-configured OVA images (templates) of Kali Linux created by Offensive Security team (Kali development team) for VirtualBox and VMware virtualization platforms.
Download the appropriate OVA template from the official Offensive Security web site. In this example, the Kali Linux VirtualBox 64-bit OVA image is downloaded.

Open VirtualBox, open Tools and click Import.

The Import Virtual Appliance wizard is opened. Browse your downloaded OVA template. In this case the name of the template file is kali-linux-2019.2-vbox-and64.ova. Hit Next to continue.

Set the virtual machine parameters by double-clicking the necessary parameter. The default VM name is Kali-Linux-2019.2-vbox-amd64 in the current example.
Define the directory in which a VM must be deployed from the template.
Select Generate new MAC addresses for all network adapters.
Tick the checkbox Import hard drives as VDI. When all VM parameters are set, click Import.

Wait for a while until the VM is imported. Then select your Kali VM deployed on VirtualBox from the template and hit Start.

The default login is root and the default password is toor for Kali Linux installed on VirtualBox from the template. VirtualBox Guest Additions are pre-installed in this case. You can use a VM with Kali Linux deployed from a VM template similarly as you use the Kali Linux VM you have created and configured manually on VirtualBox.
Conclusion
Installing Kali Linux on VirtualBox is not a difficult process, but does include a set of crucial features that you need to know. Today’s blog post has explored how to install Kali Linux on VirtualBox as a VM manually and by using an OVA VirtualBox VM template. Manual installation allows you to select your favorite Linux graphical user interface (GUI) as well as configure all necessary parameters such as virtual disk size, disk partitioning etc.
Semi-automatic installation of Kali on VirtualBox by using the VM template helps you save time, allows you to set the main VM options and deploy multiple similar VMs in a short time. You can install Kali Linux on VirtualBox on your laptop, attach an external USB wireless network adapter to the VM, and perform security testing, auditing Wi-Fi networks, and many other penetration testing tasks. You can easily switch between your host OS and Kali Linux (guest OS). Kali Linux on VirtualBox VM is isolated, meaning that you can have an adequate level of security and never need to worry about your host OS being accessible from the outside during penetration testing with Kali. You are welcome to continue learning about this topic by reading our blog post about installing Kali Linux on VMware VMs.












