Service-Oriented Architecture – GeeksforGeeks
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) is a stage in the evolution of application development and/or integration. It defines a way to make software components reusable using the interfaces.
Formally, SOA is an architectural approach in which applications make use of services available in the network. In this architecture, services are provided to form applications, through a network call over the internet. It uses common communication standards to speed up and streamline the service integrations in applications. Each service in SOA is a complete business function in itself. The services are published in such a way that it makes it easy for the developers to assemble their apps using those services. Note that SOA is different from microservice architecture.
- SOA allows users to combine a large number of facilities from existing services to form applications.
- SOA encompasses a set of design principles that structure system development and provide means for integrating components into a coherent and decentralized system.
- SOA-based computing packages functionalities into a set of interoperable services, which can be integrated into different software systems belonging to separate business domains.
The different characteristics of SOA are as follows :
o Provides interoperability between the services.
o Provides methods for service encapsulation, service discovery, service composition,
service reusability and service integration.
o Facilitates QoS (Quality of Services) through service contract based on Service Level
Agreement (SLA).
o Provides loosely couples services.
o Provides location transparency with better scalability and availability.
o Ease of maintenance with reduced cost of application development and
deployment.
There are two major roles within Service-oriented Architecture:
- Service provider: The service provider is the maintainer of the service and the organization that makes available one or more services for others to use. To advertise services, the provider can publish them in a registry, together with a service contract that specifies the nature of the service, how to use it, the requirements for the service, and the fees charged.
- Service consumer: The service consumer can locate the service metadata in the registry and develop the required client components to bind and use the service.
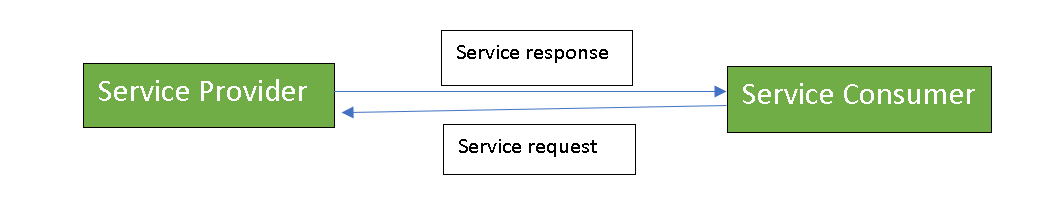
Services might aggregate information and data retrieved from other services or create workflows of services to satisfy the request of a given service consumer. This practice is known as service orchestration Another important interaction pattern is service choreography, which is the coordinated interaction of services without a single point of control.
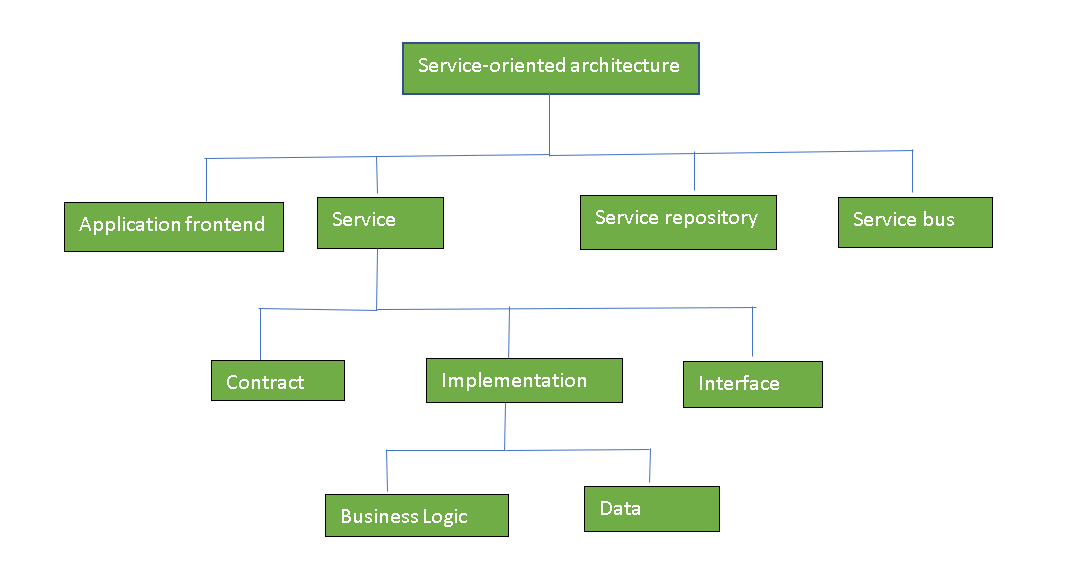
Components of SOA:
Guiding Principles of SOA:
- Standardized service contract: Specified through one or more service description documents.
- Loose coupling: Services are designed as self-contained components, maintain relationships that minimize dependencies on other services.
- Abstraction: A service is completely defined by service contracts and description documents. They hide their logic, which is encapsulated within their implementation.
- Reusability: Designed as components, services can be reused more effectively, thus reducing development time and the associated costs.
- Autonomy: Services have control over the logic they encapsulate and, from a service consumer point of view, there is no need to know about their implementation.
- Discoverability: Services are defined by description documents that constitute supplemental metadata through which they can be effectively discovered. Service discovery provides an effective means for utilizing third-party resources.
- Composability: Using services as building blocks, sophisticated and complex operations can be implemented. Service orchestration and choreography provide a solid support for composing services and achieving business goals.
Advantages of SOA:
- Service reusability: In SOA, applications are made from existing services. Thus, services can be reused to make many applications.
- Easy maintenance: As services are independent of each other they can be updated and modified easily without affecting other services.
- Platform independent: SOA allows making a complex application by combining services picked from different sources, independent of the platform.
- Availability: SOA facilities are easily available to anyone on request.
- Reliability: SOA applications are more reliable because it is easy to debug small services rather than huge codes
- Scalability: Services can run on different servers within an environment, this increases scalability
Disadvantages of SOA:
- High overhead: A validation of input parameters of services is done whenever services interact this decreases performance as it increases load and response time.
- High investment: A huge initial investment is required for SOA.
- Complex service management: When services interact they exchange messages to tasks. the number of messages may go in millions. It becomes a cumbersome task to handle a large number of messages.
Practical applications of SOA: SOA is used in many ways around us whether it is mentioned or not.
- SOA infrastructure is used by many armies and air forces to deploy situational awareness systems.
- SOA is used to improve healthcare delivery.
- Nowadays many apps are games and they use inbuilt functions to run. For example, an app might need GPS so it uses the inbuilt GPS functions of the device. This is SOA in mobile solutions.
- SOA helps maintain museums a virtualized storage pool for their information and content.
My Personal Notes
arrow_drop_up











