What Is a Proof of Concept (PoC) in Software Development? – Miquido Blog
Got a fantastic new product idea for a software development project? Great! But that’s only the first step on the journey to getting it created in reality. Research shows, however, that as much as 66% of software projects fail. How can you avoid falling into this category?
The answer is proper preparation and planning throughout the development process in the form of a Proof of Concept. Find out what a proof of concept is in software development, and why is is crucial for your next project.
What is PoC?
PoC definition
Proof of Concept, also known as PoC, is a term referring to the evidence gathered from an initial pilot project that is used to demonstrate that a theoretical idea for a project is achievable. PoCs are used in a wide range of different industries for different use cases which can include product development, business plans and more.
The PoC shows how a product idea can be launched, how it should function, and what it takes to achieve the desired goal.
The primary purpose of Proof of Concept
The main objective of a PoC is to determine how a business idea can be turned into reality and whether it is technically feasible. In this product development phase, you are focusing on something other than market requirements or competitors. Although the PoC seems insignificant, it is crucial in facilitating the subsequent stages of your product software development, such as prototyping and MVP. The Proof of Concept is also intended to help determine the direction you are taking with your product concerning other things like the chosen software system, technical specifications, or further development of your project.
The use of Proof of Concept
Many industries apply PoC for different use cases, including product development processes, business plans, and more. PoC can be used in many fields, such as software development, science, engineering sectors, marketing, or medicine.
Regardless of the industry, PoC can help the product owner or project manager identify potential technical issues right at the very beginning of product software development.
The use of Proof of Concept in software development projects
PoCs are also used in software development to determine whether the software product can be created in reality, what tools and resources will be needed in the development stage and whether it actually suits the needs of the intended users. PoC is essentially an experiment to see if the idea for the software is feasible in the real world, in the same way that products are trialled before reaching development.
Think about it this way, a new type of shoe wouldn’t be rolled out to the public until it had been tried and tested first. The shoe company would have to prove that the shoe is a good product-market fit, is fit for purpose and liked by customers, and that it could be made with no faults. A software product PoC works in the same way. If you had a great idea for a new app you’d like to launch, you would first need to make sure it could be built, that it was needed and worked for users, and that there were no technical errors.
Your PoC should be created after you’ve fully developed and defined your idea. You should already have a solid plan of where you’re headed before the PoC. The PoC is the first step in the technical implementation of the concept.
1 month for a ready-made PoC?
Join Product Bootcamp!
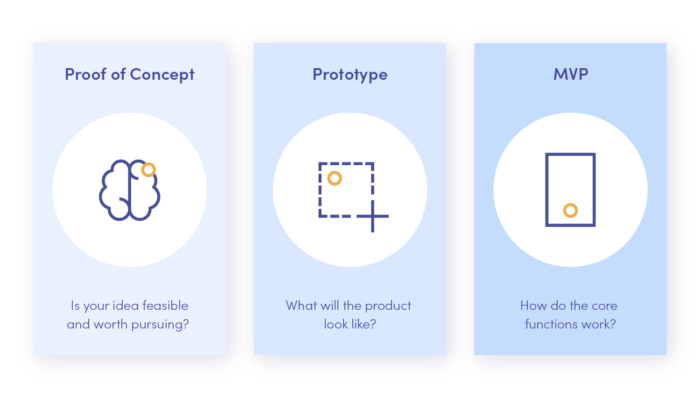
Differences between Proof of Concept, Prototype and MVP
These three terms, although often equated, refer to different stages in the product development lifecycle.
Prototype in the development process
While the Proof of Concept is to visualise how the product can work in the market and solve real-life problems of your potential customers, the prototype is a step further. It aims to test the planned functionality and detect problems in the functioning or design of the product. Using a prototype, you can also present it to potential users to get valuable feedback from testing your digital product. In other words, the prototype is a more advanced version of the Proof of Concept.
Minimum Viable Product in the development process
Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is the first version of your product that you can release. It includes basic functionality and features. The purpose of an MVP is to see how the market will react to the product, allowing you to test it with real users. It is a great way to find bugs and refine your product to meet customer expectations. The MVP is, therefore, a significantly extended version of the prototype.
Unlike a PoC and prototype, creating a good MVP requires a lot of time. It takes just a few days to develop a Proof of Concept. Building a prototype requires a few weeks of work, and making an MVP takes at least a few months.
The benefits of Proof of Concept in software development
Now you know what a PoC is, but what is the point of creating one in the first place? There are a number of benefits that make drafting a PoC a great idea for your next project.
Insights from key stakeholders
A successful PoC is great for helping to gather feedback from key stakeholders involved in the project at an early stage. Once they can see the software solution in action, they’ll be able to provide feedback throughout. It’s beneficial to capture this feedback early, before full development, to allow flexibility and room for adjustments before it’s too late. Both positive and constructive feedback can be incredibly helpful in making sure that the project is heading in the right direction.
Insights from developers
Proof of Concept also allows the software development team to offer feedback and insights about the technical aspects of the software. As the ones that will be actually building the software, they can actually test it to see if it’s technically possible. If not, you can go back to the drawing board and develop your concept so that it’s ready for development.
Increased communication and efficiency
There is a strong correlation between a good PoC and improved efficiency during project work. Firstly because participants in the Proof of Concept phase have better insights into current problems and challenges and this enables them to respond to difficulties. It is much easier to wrestle with issues when they are clearly articulated. In addition, everyone can bring a completely different perspective to the design process, which increases the effectiveness of the PoC.
Demonstrate market-fit
A Proof of Concept defines the target market need for the software and demonstrates what problem it will solve and how it will do so. To demonstrate this in the PoC, you’ll need to carry out research with your intended audience. This helps prove, rather than just speculate, that your software will be received positively by your target users – minimising the risk that your software idea won’t be successful upon launch. Getting user feedback can also help you to flag any issues your team may not have spotted themselves.
Cost-effective approach
Creating a Proof of Concept can be far more cost-effective in the long run. Without a PoC, you risk choosing wrong technology solutions or spending lots of time developing features that don’t work or aren’t needed. These stages of development can quickly become very expensive – especially if you have to account for issue-correction or major changes to the plan. Instead, it’s much better for your budget if you develop a PoC before you start on the actual product.
More accurate project plan
A PoC also allows you to more accurately plan your project. It will give you a much clearer understanding of the time, resources, effort and costs involved, and will allow you to manage them accordingly. This will prevent surprises like delayed timeframes or the need for extra resources.
How to create a successful Proof of Concept
A given Proof of Concept can be vastly different from any other PoC since they follow no set structure or rules. A PoC can be created as a text document, presentation or demo and can be updated as you develop the project and receive feedback.
For the software development process, you can start creating your own PoC by following the steps below:
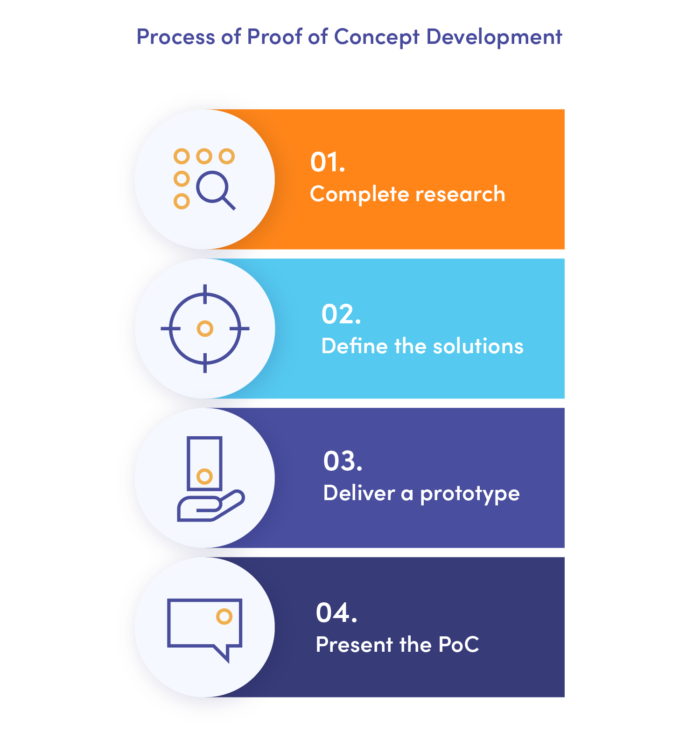
1. Complete research and prove the market need
In this phase you need to demonstrate two main things: what problem exists that you’re trying to solve; how you’re going to do it. Just explaining them isn’t enough however, you need to prove your idea is feasible. Lay out the exact pain point your target audience experiences and conduct research to support – you could speak to a small representative working group for example. Identity any patterns and use the insights to define what your software needs to include.
Check these useful market research methods and techniques – with them, you will be able to gather correct market insights.
2. Define the solutions
Using your newly gathered feedback and insights, start matching them to solutions as part of your concept. Come up with ideas on how you can solve their pain points using the final product. Once you’ve come up with your solutions, refer back to your initial research group and analyse their responses to see if you’re on the right track.
3. Deliver a prototype
Next, create a prototype of your solution based on the decided software features. Once you’ve done this, test the prototype on your sample group to verify whether it addresses their pain points in actuality. Document all of this to demonstrate the usability and technical feasibility of the software.
4. Present the PoC
Involve all key stakeholders and present them with with a clearly-defined Product Roadmap for their approval, feedback and insights. It should include the research you conducted, how the product solves the identified problems, as well as details on the features and the technologies used in the development.
The Proof of Concept phase is, therefore, crucial to the development of your project. It is worth implementing a PoC in your company, as this solution can significantly reduce costs and product development time, maximising efficiency. Get your own Proof of Concept in just 2-4 weeks by partnering with our software development company. Through extensive market research, idea validation and the rapid prototype development of your product, we’ll test out whether your ideas can be achieved and what needs to be improved and/or changed about it.











