What is BIM (Building Information Modeling) & BIM Software
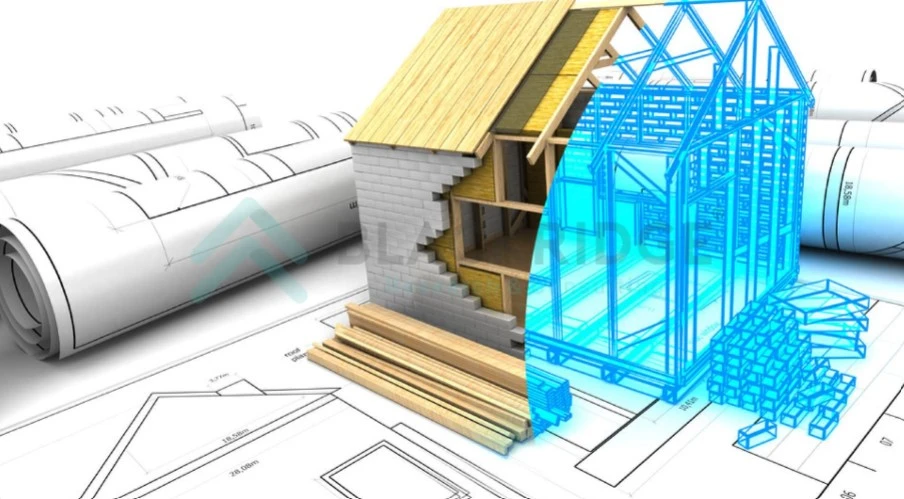
Building Information Modeling or BIM is a 3D model-based concept used by construction professionals for AEC (Architecture Engineering Construction) projects. BIM model helps AEC professionals visualize 3D modeling of the structures before their actual construction starts and allows them to collaborate on a project’s design and construction efficiently.
It helps in the creation of multidimensional models that include information on functional features as well as physical aspects. This technology is widely implemented in many industries, including but not limited to civil engineering, plant management, mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, plumbing systems, HVAC, and structural design.
Mục lục bài viết
What is BIM?
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a cutting-edge technology that aids architects, engineers, and construction professionals in infrastructural facility planning, design, construction, and construction management.
The US National Building Information Model Standard Project Committee has the following definition:
“Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of physical and functional characteristics of a facility. A BIM is a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility forming a reliable basis for decisions during its life-cycle; defined as existing from earliest conception to demolition.”
BIM may appear to be a tool for creating 3-D infrastructure models. But it is more than merely a tool. It’s an entire technology in itself. It is a technological process where the key stakeholders of a construction project can easily collaborate throughout the life cycle of a construction facility.
This high-tech modeling technology reflects a more extensive database relating to every aspect of the construction project. Therefore, BIM integrates the five essential phases of a project in such a way that the overall scope of the project is met effectively. These five aspects are:
- The Initiation Phase
- The Pre-Construction Phase
- The Procurement Phase
- The Construction Phase
- The Post-Construction/ Closeout Phase
Recent advancement in BIM has resulted in the creation of 4D BIM, 5D BIM, and even 6D BIM solutions. Besides the features of any civil 3D model that visualize width and depth, these new BIM objects can predict project timeline, construction costs, and operational challenges.
Understanding BIM technology
The concept of BIM modeling has been in various phases of development since the 1970s. But it came to its present form only in the 2000s when the standards and processes of the BIM process were adopted worldwide.
AEC projects are becoming more complex due to global trends, while technological improvements in structural engineering are enabling industry professionals to design, build, and operate more effectively. Among these advancements, building information modeling software has proved to be a revolutionary tool in the AEC construction industry and project management.
BIM services allow designers to construct a digital 3D BIM model of a structure before it is built. Furthermore, the BIM data includes information about the structure’s physical and functional qualities that ultimately help in better decision-making.
When architects, engineers, and contractors can work together on a collaborative architectural design using open BIM, they understand how their work fits into the bigger picture and can accomplish more in less time.
BIM software provides insight into a design’s constructability, increasing the construction phase’s efficiency and usefulness and offering a better understanding of the building’s future operations and maintenance. Owners can use the BIM tool for preventive maintenance, asset tracking, facility management, and future restoration.
CAD vs. BIM
CAD

CAD or Computer-Aided Design uses computers to prepare 2D and 3D designs of buildings and structures. It is more of a drafting tool that is majorly used in designing. CAD software like Autodesk Revit software initially allows the creation of 2D drawings, including floor plans, walls, and building layouts. However, software packages have evolved in recent years.
BIM
BIM, or Building Information Modeling, is a data-rich information database rather than just traditional CAD drawings. It shares data with all construction project stakeholders through intelligent BIM models. Since it relies mainly on visual information, it connects the disconnected silos of information among the involved parties in a project.
Various software like Bentley’s OpenBuildings Designer or Vectorworks Architect combines CAD and BIM tools to create more information-rich models.
Note: Silo is an isolated program, system, department, or organization that works independently without communicating or collaborating with others.
What does BIM promise?
BIM software promises to develop a structure before physically constructing it virtually. This enables project participants to plan, analyze, sequence, and explore a project in a digital environment. Making changes to the design in a digital environment is significantly less expensive than the actual construction, where changes are complex and very expensive.
Additionally, an array of BIM software, tools, and mobile apps produce outcomes that reduce construction risk. This is made possible because the BIM data in a 3D model defines the design elements and model components.
Any change in one element in a model changes the section, elevation, and sheet views. You can use the information in the model to improve your design before it’s built, thereby improving timelines, saving costs, and overall project outcomes.
How is BIM used during the design and construction phase of a building/facility?
Engineers utilize BIM software such as Autodesk construction cloud, BricsCAD bim, and Autodesk Navisworks to design and build modern structures. Here is how it helps achieve the highest levels of efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness in the design and building process, a variety of techniques and procedures.
Step 1: Modeling
Architects use BIM authoring tools to make detailed 3D models of the structure. They can experiment with the design and identify potential issues at this stage before committing their ideas to the construction process.
Step 2: Workflow
All information and ideas related to the project are stored in a shared location that clients, architects, contractors, and other collaborators can access. This is usually a cloud-based software, meaning anyone with secure permissions can access it from any location by connecting to the server. Architects can use BIM software to make design choices and calculations like:
- Energy and light analyses
- Spatial planning
- Parametric modeling
- Material choices
- Cost estimations
- Construction time estimations
Using these models and estimates, architects can lay out the most efficient construction workflow for the project.
Step 3: Construction
With the established workflow in mind, contractors (with support from the architecture firm) construct the building. They can revisit the BIM model or workflow anytime during the process and adjust as needed. One of the benefits of BIM is that it keeps everyone on the same page during construction, even when the workflow changes.
Step 4: Handover
After the structure is complete, architects can turn over the BIM model to the client or the facility management (FM) company. A detailed design model helps locate HVAC systems or make future renovations.
Various Levels of BIM
Level 0
Level 0 projects encourage zero collaboration and use paper-based 2D CAD drafting approaches. The primary purpose is to generate production information on paper or electronic devices. This is an obsolete level that industry professionals rarely use nowadays.
Level 1
Level 1 is an up-gradation of Level 0. Designers use 3D CAD for conceptual works and 2D CAD for generating statutory approval documents and Production Information. Nevertheless, it is the partial collaboration stage between different BIM project stakeholders.
Every party in Level 1 creates and manages its own data and does not share it unless it is required. A significant feature is the use of the Common Data Environment or CDE like Autodesk BIM 360 when the teams collaborate to share building data.
Level 2
Level 2 BIM is generally used for public sector projects. This level is the real beginning of collaborative working by the stakeholders who are given their own 3D CAD models.
Level 2 requires seamless coordination between all the parties and systems for streamlined information exchange that results in a shared 3D model. This level requires the use of a common file format like Industry Foundation Class or IFC.
Note: Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) is a file format for CAD data exchange. It is a decentralized (not controlled by any single entity) open file format, widely used for its interoperability for developing BIM projects.
Level 3
Level 3 is the ultimate collaborative level where all the stakeholders of a construction project work on a shared model located in a central vault. This level is often termed Open BIM. Level 3 allows the participants to work simultaneously on the same building model which eliminates the chances of discrepancies in the shared information.
Level 3 also encourages the use of open file formats like IFC to eliminate the possibility of conflicting information. This level includes 4D BIM (construction sequencing), 5D BIM (cost), and 6D BIM (post-construction facility management information).
Understanding the dimensions of BIM
3D BIM
Three-dimensional building information modeling or 3D BIM is the graphical representation of a structure’s geometric design which is supplemented by other essential information related to the individual components of the facility.
It is important to have a point cloud for creating virtual 3D BIM models. A point cloud is a database that stores a facility’s spatial data, which can be easily scanned and used for 3D modeling. While creating 3D BIM models, designers consider three important professional disciplines: structure, architecture, and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing).
4D BIM
4-dimensional building information modeling or 4D BIM is the intelligent linking of a fourth dimension, i.e., time, with the 3D BIM models.
4D BIM modeling allows all the project participants (designers, architects, contractors, project owners, and clients) to plan the sequence of various physical activities in the construction process. Since the participants can visualize the series of events early in the planning stage, they can mitigate any possible risks that might come during the post-construction phase as well.
5D BIM
5-dimensional building information modeling or 5D BIM is the intelligent linking of a fifth dimension, i.e. costs along with all other dimensions of 4D BIM models.
Apart from the benefits of a 4D model, a 5D model allows project participants to picturize the construction progress and the subsequent costs over time. Having the knowledge of the cost components associated with the project in advance, project owners can precisely make the cost estimation and if needed, raise capital for large-scale construction projects.
6D BIM
6-dimensional building information modeling or 6D BIM is the intelligent linking of a sixth dimension, i.e. information regarding the post-construction facility management along with all other dimensions of 5D BIM models.
However, 6D is the latest addition to BIM technology and it’s yet to have a wide-scale application. At the moment, 6D modeling is used for making buildings more ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) compliant and energy-efficient. The data available in 6D modeling is intended to help facility operators and managers in the smooth operation and maintenance of the facility.
Benefits of BIM software
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has become an essential technology for the building industry, providing a wide range of advantages. Every stage of the project lifecycle and beyond can be improved with the use of BIM technology.
BIM is one of the disrupting technology in the construction industry that allows the project stakeholders, primarily, architects, designers, engineers, and contractors to visualize how their contributions fit in the big picture. Apart from this, BIM software also offers several other benefits in AEC projects.
Here are 7 top-notch benefits of BIM software.
Visualize projects in preconstruction
BIM allows visualizing the entire facility or structure in the preconstruction phase. Thanks to the advanced space-use simulations and 3D visualization techniques, project stakeholders can see how the space will function and make modifications before construction even begins. Robust planning at the beginning reduces the need for subsequent changes which are not only costly but also time-consuming.
Model-Based cost estimation
AEC companies have now realized that coordinating with estimators in the pre-construction planning phase allows them to get a better construction cost estimation. Therefore, the use of model-based cost estimating (also known as 5D BIM) is increasing.
Using 5D BIM tools like Autodesk Revit and BIM 360 Docs, designers and contractors can leave the time-consuming tasks of quantifying and applying costs to these tools. Instead, they can focus on other higher-value factors like construction assemblies.
Better collaboration and coordination
Powerful structural BIM software like Teckla Structure or Autodesk’s Revit allows better collaboration and optimization of building models. These models are cloud-based and thus, seamlessly allow participants to work simultaneously. The working teams of different disciplines can collaborate together to share their project data and coordinate among themselves in the pre-planning and planning phase for the best output.
Moreover, the integration of cloud technology with BIM software lets the designers and architects access the models anywhere, be it in the office or the project site. Having the insights from all stakeholders continuously keeps the model updated with the latest information and inputs.
Avoid clashes between the different participants
BIM enables improved coordination among various disciplines and subcontractors of the project. It also detects possible internal, exterior, or MEP disputes before General Contractor or EPC contractor begins the construction work. Having seen a 3D replica of the facility, in the beginning, will substantially remove the chances of last-minute changes in the design and execution.
Mitigate risk and reduce cost
Around 75% of businesses that have implemented BIM have seen a return on their investment. But if you take advantage of BIM, you can save money in a variety of other ways like
- Tender risk premiums can be reduced
- Insurance costs can be reduced
- There will be fewer overall variations in planning and executions
- Reduction in wastage of construction materials
- Time and money spent on documentation can be cut in half
- Lower chances of expensive mistakes or last-minute modifications
- Overall labor and material costs can be reduced
Increase productivity with prefabrication
BIM helps in the instant generation of production drawings. These drawings can predict the number of prefabricated and modular units required for the building. Construction engineers and contractors can save a substantial amount of time due to the prefabrication.
Furthermore, by designing, detailing, and building offsite in a controlled environment, project owners can reduce material wastage which will, in turn, reduce the material costs.
Streamlined facility management
BIM 3D modeling data can also be used to improve the building’s operations once construction is complete, resulting in a long-term return on investment (ROI). Construction software can help facilities managers and renovators keep an accurate digital record of building information throughout the whole lifecycle of the structure.
BIM software – key takeaways
- BIM modeling isn’t limited to just geometric studies. It simultaneously analyzes spatial data, geographic information, layouts, time, cost, and management information. Building Information Modeling is also known as “Virtual Building” or “Integrated Project Models”.
- BIM models help builders figure out how many parts and how much of each material they need.
- It also helps in facility management and predictive maintenance of a structure.
- BIM plays an important role in the optimum utilization of resources and productivity enhancement. This further reduces the wastage of resources and materials.
- BIM removes silos in communication and paves the way for better coordination between the project teams. By using BIM, project participants can share construction data to accomplish the best output.
- This smart, sophisticated, and cutting-edge technology has become the backbone of architecture and development. Due to its immense impact on AEC projects, it’s surely a revolutionary technology in the construction industry.
FAQs
What does BIM mean?
Building Information Modeling or BIM is the technology to visualize a structure in 3D models with all the information and data related to the entire lifespan of the structure being available in a shared database. Various teams can communicate fluently by using BIM platforms such as BIM Track which eliminates the Silos in the organization.
Is BIM a software?
BIM is basically a technology or process of creating 3D models using various other software. These models can help in optimizing the work of different disciplines such as architecture, construction, and MEP projects. There are various vendors providing BIM software like Tekla (Tekla BIMSight & Tekla Structure and Autodesk (AutoCAD, Navisworks & Revit).
How does a BIM work?
BIM operates by applying smart insights to a building’s physical components. While a CAD design may depict the layout of a room you want to rebuild, BIM informs you of the load-bearing capacities of the walls, the best way to reroute the electrical layout, and the materials required to install the best HVAC system.
What is the difference between BIM and CAD?
BIM is a coordinated, reliable workflow that covers a project’s whole lifecycle, from conception, construction and operation. Contrary to BIM, CAD is Computer-Aided Design that mainly focuses on transforming paper-based drawing into digital formats.
Why is BIM the future of construction?
BIM makes it simple for all project participants to work together during every phase of a building’s lifecycle. The participants can acquire a highly detailed digital representation of construction designs by employing BIM. Additionally, BIM delivers other important insights like cost, timeline, and maintenance schedule of the structure in addition to just being a 3D model.
Looking at the immense popularity and enthusiastic adoption by AEC companies, it is evident that BIM is a game-changer for the AEC industry. Adding to that, even governments around the world are making the adoption of BIM mandatory for large-scale construction projects.
P.S.: Are you a general contractor or construction management firm looking for new construction project opportunities? Check out our Global Project & Tender Tracker to find a suitable project that matches your portfolio. Even for owners, it provides valuable insight into the current developments in the construction industry.











